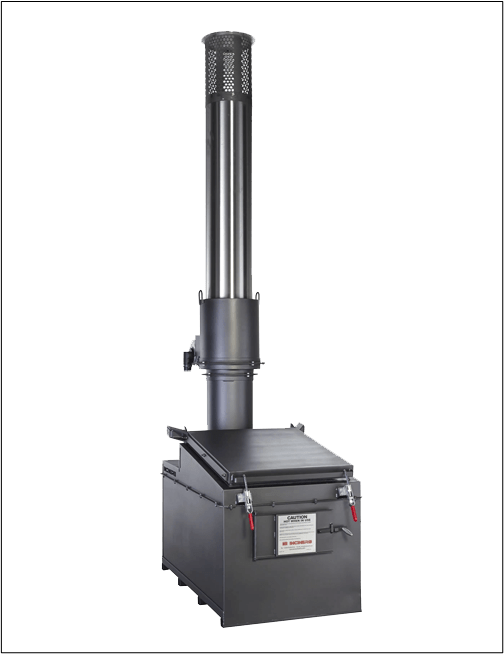
Biological Incinerator
- Introduction
- General specifications
- Technical specifications
- Physical specifications
- Waste that can be incinerated
- incineration
- Administrative procedure
Incineration is an integral part of modern waste management, enabling sustainable waste disposal while also recovering valuable energy. By burning waste at high temperatures, incinerators significantly reduce waste volumes and sterilize hazardous materials. While waste incineration has faced criticism in the past, advances in pollution control technology have significantly reduced emissions from modern incinerators. When combined with appropriate pretreatment techniques such as sorting, shredding, and drying, along with careful monitoring and maintenance, incineration allows waste management facilities to safely and sustainably handle a wide range of waste.
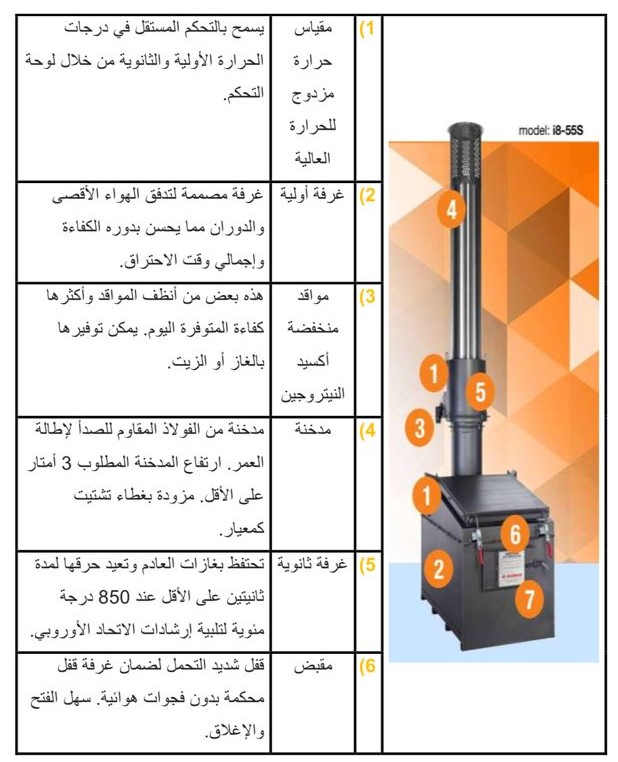
1. Easy installation and setup.
2. Fast, complete, and efficient disposal of general waste.
3. Safety handle for easy access to the chamber.
4. High-quality lining and thermal insulation.
5. User-friendly CE2 control panel.
6. Programmable temperature control for complete combustion.
7. Rapid preheating and continuous performance at high temperatures.
8. Low energy consumption levels.
9. Secondary chamber with a 0.5-second retention time.

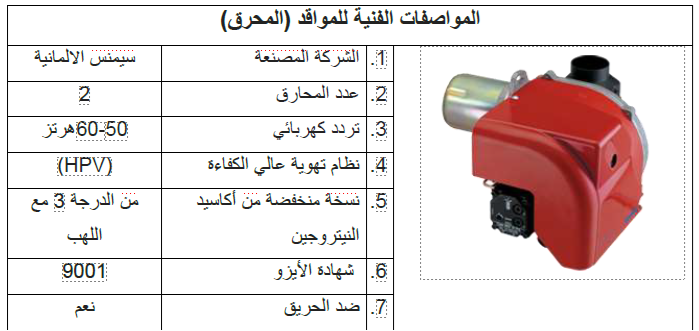
| No. | Specifications | Details | ||||||
| 1 | Manufacturer | UK | ||||||
| 2 | The model | i8-55s Multi-Purpose Incinerator | ||||||
| 3 | Combustion chamber volume | 0.36 M³ | ||||||
| 4 | Burn rate | 40 kg per hour (*varies depending on waste type and operating conditions*) | ||||||
| 5 | Average fuel consumption | 10–12 liters per hour (fuel type: gas/oil). | ||||||
| 6 | Operating temperature | Above 850°C. | ||||||
| 7 | Gas retention time in secondary chamber | 0.5 Sec. | ||||||
| 8 | temperature monitoring | Available | ||||||
| 9 | Average ash residue | 3%. | ||||||
| 10 |
thermometer |
Temperature control stabilizer |
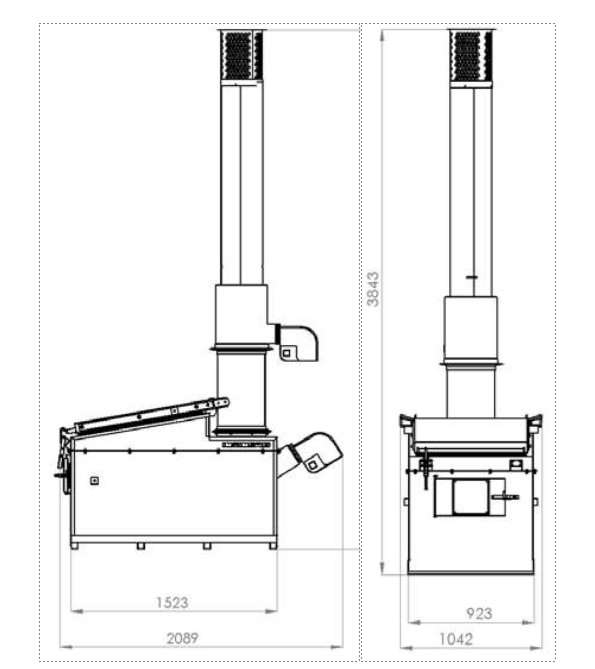
| No. | Specifications | Details | ||||||
| 1 | length | 1520 mm | ||||||
| 2 | width | 920 mm | ||||||
| 3 | height | 4020 mm | ||||||
| 4 | Gate opening size | 720 mm× 830 mm. | ||||||
| 5 | Shipping weight | 1670 kgm |
Many types of waste can be incinerated instead of being buried in landfills. The most common waste in incinerators includes:
1- Carcasses of dead animals.
2- Biological waste from laboratories (such as needles, blood products, and anatomical waste).
3- Waste from microbiology laboratories (such as bacterial dishes, culture media, virus and bacteria samples, and molds).
1. Sorting - removing any high-value recyclable materials for resale.
2. Shredding - normalizing particle size and adding air to the mix.
3. Drying - We recommend a maximum humidity of 30% to ensure optimal efficiency.
4. Batch Sizing - optimizing batch size to achieve the lowest costs in the shortest time.
5. Ash Removal - removing ash from the system in preparation for the next batch.
6. Random Inspection - ensuring that the chamber, burners, and fuel lines are all in good condition.
7. Reloading - loading the chamber for the next process.
Important Notes: - Burning rates depend on the calorific value of the waste, atmospheric conditions, and fuel quality.
First, register via the request form for destruction or incineration of biological samples.
Second, after obtaining approval from the relevant committee, the researcher will be provided with a quick response code (QR code).
Third, examine and inspect the samples by the incinerator operator.
Fourth, bring the samples into the main incineration chamber for destruction.
Details of the incinerator
The waste is loaded and ignited. Ignition occurs due to the high ambient temperatures maintained within the chamber lining.